Designating NICs for HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric
Explains how to assign IP address blocks for HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric.
By default, file-system instances and the CLDB nodes advertise all the available IP addresses, and HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric automatically uses all available network interface cards (NICs) on each node for all communication. For nodes that have multiple NICs, HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric supports segregation of the NICs. Segregation enables certain IPs to be used for clients or communication within the cluster, and certain IPs can be used for clients or communication from outside the cluster. Also, NICs can be segregated for specific (high-performance and/or low-performance) clients within the cluster.
For example, if you use multiple NICs of mixed speeds (such as 1GbE and 10GbE) on each node, you might want to separate them to two different networks depending on the Ethernet card speeds. You can assign IP addresses in the same network to the NICs of 1GbE and assign IP addresses in another network to the NICs of 10GbE. In this way, you can use the faster NICs for communication within the cluster or for certain high-performance clients (for example, FUSE-based POSIX clients) and the slower NICs for external communication or for low-performance clients or jobs.
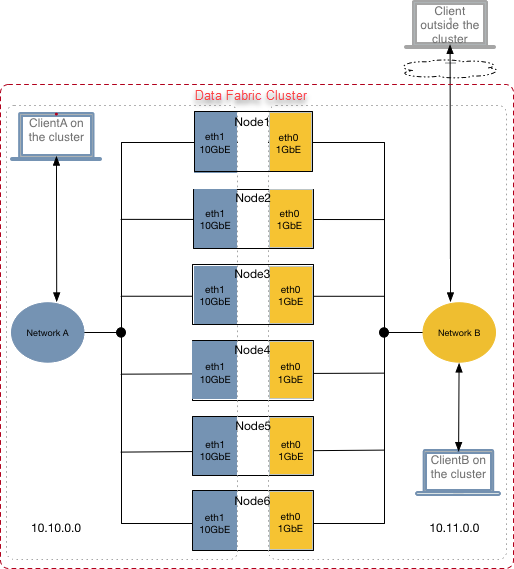
To illustrate this arrangement, the following diagram shows six nodes on an HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric cluster, each with a 1GbE NIC (eth0) and a 10GbE NIC (eth1). All the 1GbE NICs are networked together and connected to Network B. Likewise, all the 10GbE NICs are networked together (as part of a subnet written as 10.10.10.0/24 in CIDR notation) and connected to Network A, where peak performance is required. ClientA, which is within the cluster, communicates with cluster nodes over Network A. Clients outside the cluster communicate with cluster nodes over Network B.
The illustration also shows ClientB, which is a low-performance client inside the cluster, communicating with cluster nodes over Network B:
HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric provides two environment variables,
MAPR_SUBNETS and MAPR_EXTERNAL, that you can use to
segregate NICs for internal and external clients or to segregate NICs for high-performance and
low-performance clients.
MAPR_SUBNETS Environment Variable
MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable can be used to restrict HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric to a subset of NICs. If MAPR_SUBNETS is not set, all IPs are
available for all communication. The following table describes the behavior when
MAPR_SUBNETS is set on:| Node Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| File System | The file system registers these IP addresses with CLDB as internal IP addresses on which file-system nodes can be reached. |
| CLDB | The CLDB advertises the IP address to clients on the cluster. |
You can set the MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable in the
/opt/mapr/conf/env_override.sh file on all the nodes. On the cluster
nodes, the value for this environment variable is a comma-separated list of subnet masks.
For example:
export MAPR_SUBNETS=10.10.15.0/24,10.10.16.0/24You can specify up to four NICs in the MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable.
If your system has more than four NICs, HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric advertises the first four it finds.
Or, if the MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable is set, HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric
restricts the networks or IPs that are advertised based on the subnets specified
therein.
The MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable can be set on the client if there is
a NAT between the server and client. On the client, the value for this environment variable
is the IP address of the client. For example:
export MAPR_SUBNETS=10.11.12.13/32When specifying the IP address in the MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable on
the client, use /32 to specify a single IP address.
For more information about the MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable, see Environment Variables.
MAPR_EXTERNAL Environment Variable
If all the IP addresses on the servers are public and can be accessed from an external
system, the MAPR_EXTERNAL environment variable need not be set. However, if
your cluster nodes have private IP addresses, to allow clients outside the cluster to reach
the cluster nodes (such as when data-fabric is installed on the cloud or Docker container), specify the public IP
addresses in the MAPR_EXTERNAL environment variable.
/opt/mapr/conf/env_override.sh file. The following table describes the
behavior when MAPR_EXTERNAL is set on:| Node Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| File System | The file system registers these IP addresses with CLDB as the IP addresses on which external clients can reach file system nodes. Communication between file system nodes on the cluster still occurs over the internal IP addresses. |
| CLDB | The CLDB advertises these IPs addresses to clients outside the cluster or data center. |
| MAST Gateway Nodes | The gateway registers these IP addresses with the CLDB as the IP addresses on which external clients can reach the MAST Gateway. |
MAPR_EXTERNAL environment variable on client(s).The value for this environment variable is a comma-separated list of IP addresses. You cannot specify the hostname as value. For example:
export MAPR_EXTERNAL="10.0.0.101,3.87.212.119"
export MAPR_SUBNETS="172.31.00/16"For example, you can specify the IP addresses of the 1GbE NICs (shown in the previous illustration) as the value for this environment variable, to allow external or low-performance clients to communicate with the cluster nodes.
export MAPR_EXTERNAL=10.11.0.0For more information about the MAPR_EXTERNAL environment variable, see Environment Variables.
IP Addresses for ZooKeeper Nodes
-Z and
-EZ options during cluster configuration. The following table summarizes
how to use these options: | When using this option | You specify |
|---|---|
-Z |
Internal IP addresses |
-EZ |
External IP addresses |
When you specify the IP addresses using the -Z and -EZ
options, these IP addresses are registered with the CLDB and included in the
cldb.conf file. In the cldb.conf file, the internal IP
addresses set using the -Z option are the values for the
cldb.zookeeper.servers parameter. The external IP addresses set using the
-EZ option are the values for the
cldb.external.zookeeper.servers parameter.
configure.sh command with the
-EZ option during client configuration.For more information, see configure.sh.
If all the ZooKeepers have different IP addresses, port forwarding is not required and,
optionally, you can specify the same port with all the IP addresses. However, in some cases,
such as when a single external IP address is used by multiple ZooKeepers (as in a Docker
container), you can specify ports for ZooKeepers when you run the
configure.sh utility with the -Z and
-EZ options. For more information, see Specifying Ports.
Internal and External Clients
Clients communicating with the the CLDB using internal IP address (of CLDB) are considered internal clients (or clients within the cluster). Clients communicating with the CLDB using external IP address (of CLDB) are considered external clients (or clients outside the cluster).
To configure a client as an internal or high-performance client, include the CLDB internal
IP address in the mapr-clusters.conf file on the client host. Similarly, to
configure a client as an external or low-performance client, include the CLDB external IP
address in the mapr-clusters.conf file on the client host.
The mapr-clusters.conf file on the client host should not contain both
internal and external IP addresses of the server on a cluster. The
mapr-clusters.conf file can contain internal and external IP addresses
only when the entries in the file on the client host are for multiple clusters.
For example, suppose you have a client, which is an internal client on one cluster and
external client on another cluster. The mapr-clusters.conf file on the
client host can contain the CLDB internal IP address for the cluster on which the client is
considered an internal client and the CLDB external IP address for the cluster on which the
client is considered an external client.
mapr-clusters.conf file on the cluster nodes should not contain any
external IP address.Limitations
Note the following limitations for using the environment variables:
- If both
MAPR_SUBNETSandMAPR_EXTERNALenvironment variables are set, the segregation of NICs for internal and external communication is possible. Internal communication happens over the IP addresses listed in theMAPR_SUBNETSenvironment variable, and external communication happens over the IP addresses listed in theMAPR_EXTERNALenvironment variable. - If only the
MAPR_SUBNETSenvironment variable is set, the file system registers the IP addresses in theMAPR_SUBNETSenvironment variable with the CLDB as internal IPs.NOTE To segregate internal or high-performance clients, and external or low-performance clients, set both the environment variables in the/opt/mapr/conf/env_override.shfile. - You can specify up to four IP addresses in the
MAPR_SUBNETSenvironment variable, and four IP addresses in theMAPR_EXTERNALenvironment variable. - You must configure ZooKeeper with an IP address that is reachable by both internal and external clients.
- Do not run any of the following clients in a Docker image on a
host server with multiple NICs:
- File-system, database, or Marlin clients
- NFS server variants
- Applications using the
mapr-clientlibrary
Summary
The following table describes the environment variables to set for the various services that use non-default ports and that support public IP address(es) for communication with external clients and remote clusters:
| Service | Environment variable to set... | |
|---|---|---|
| Public IP Address for External Clients/Remote Clusters | Non-default Port | |
| CLDB | MAPR_EXTERNAL |
CLDB_EXTERNAL_RPC_PORT |
| File System | MAPR_EXTERNAL |
MAPR_EXTERNAL |
| MAST Gateway | MAPR_EXTERNAL |
MASTGATEWAY_EXTERNAL_RPC_PORT |
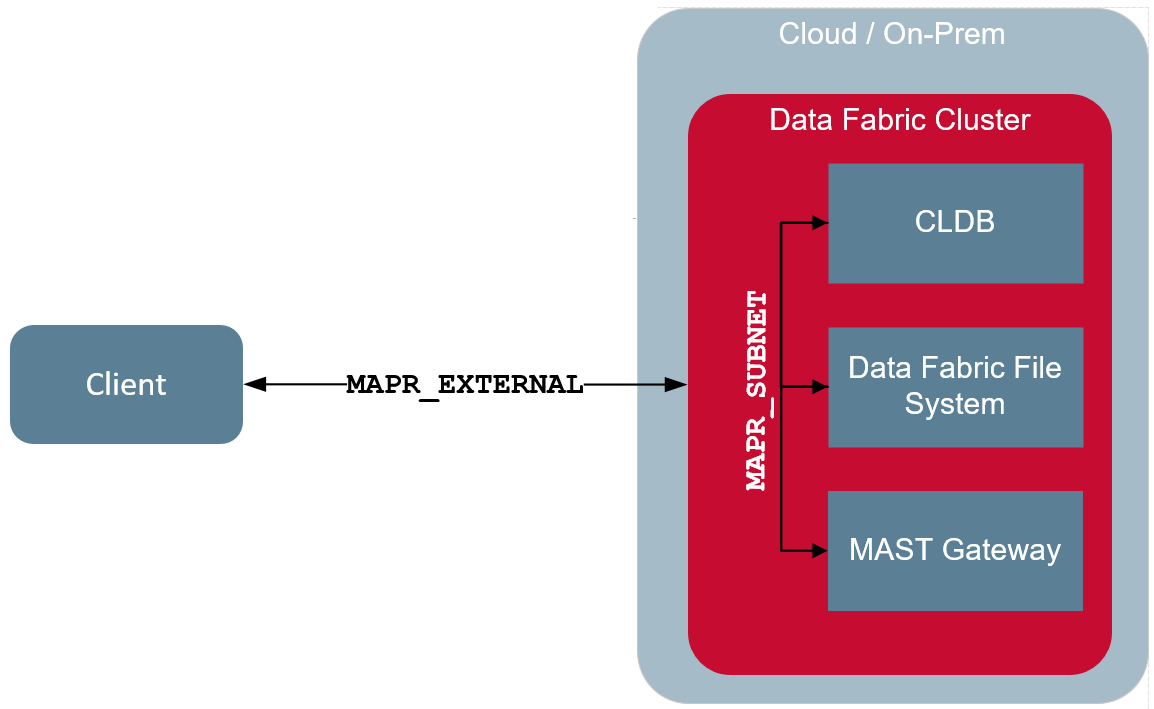
The following illustration shows the client communicating with the CLDB, HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric file system, and MAST Gateway using the IP address(es) defined in the
MAPR_EXTERNAL environment variable. This is because all the IP addresses
on the servers are not public and accessible outside the cluster. All communication between
CLDB, file system, and MAST Gateway on the same cluster happen
over the IP address specified in the MAPR_SUBNETS environment variable.
This is because communication between the services and clients on the cluster is restricted
to a subset of the available NICs.
When the client connects to the HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric file system from outside the cluster,
the client uses either the default port (5660) or the port specified for the data-fabric file system in the
MAPR_EXTERNAL environment variable.
When communicating with the CLDB, if the CLDB_EXTERNAL_RPC_PORT
environment variable is set, the client communicates with the CLDB over the port specified
in this environment variable. Similarly for MAST Gateway, if the
MASTGATEWAY_EXTERNAL_RPC_PORT environment variable is set, the client
communicates with MAST Gateway over the port specified in this environment variable. For
both CLDB and MAST Gateway, if the ports are not set in the
CLDB_EXTERNAL_RPC_PORT and MASTGATEWAY_EXTERNAL_RPC_PORT
environment variables respectively, the client communicates over the default port.
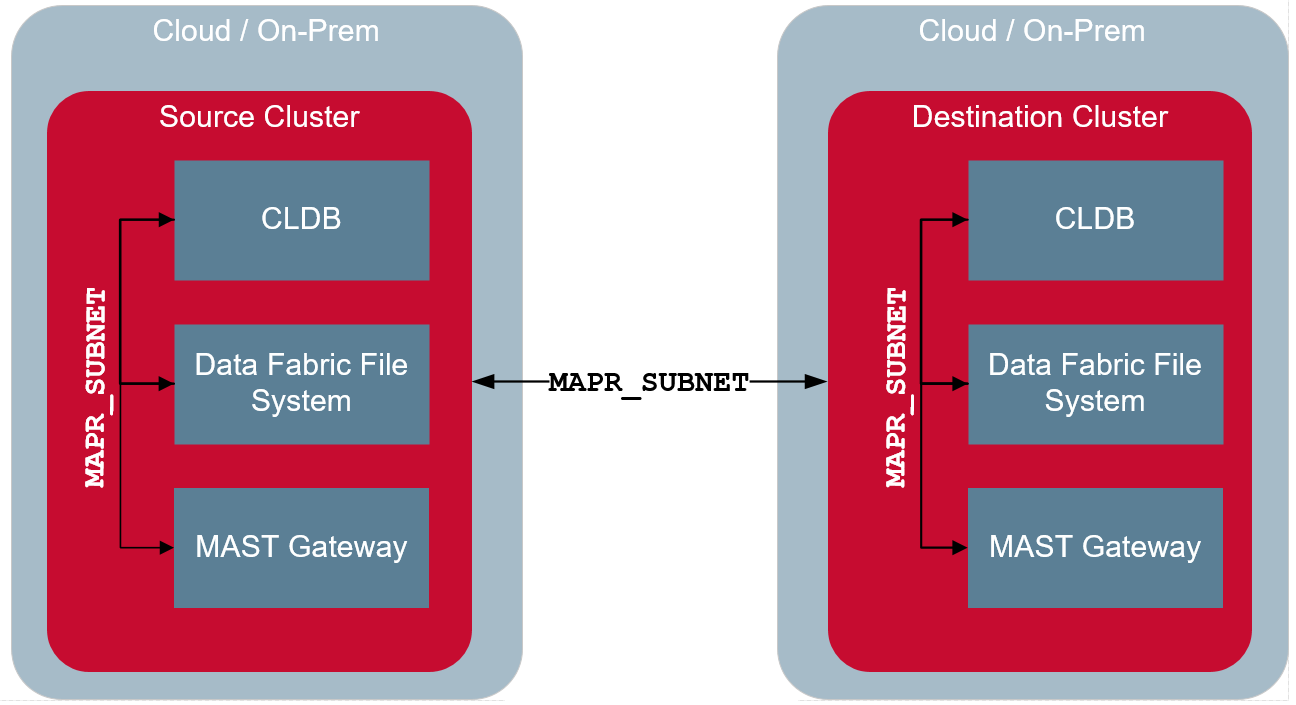
The following illustration shows that during mirroring and other cross-cluster activities,
the services on the destination cluster communicate with the services on the source cluster
using the IP address defined in the MAPR_EXTERNAL environment variable. As
with the external client, the services and clients in the remote destination cluster
communicate with the services in the source cluster over the default ports or the port
specified in the environment variable for the service.