Managing Hard Links
Explains what hard links are, and their limitations.
A hard link is a directory entry that associates a name with a file (or physical data) on the filesystem. Hard links allow multiple names to be associated with the same data (and associated inode) from within or outside of a directory. Every time a hard link is created, a directory entry is created and the inode (associated with the directory entry) remains the same across all hard links associated with that data. That is, all names associated with the data point to the same inode.
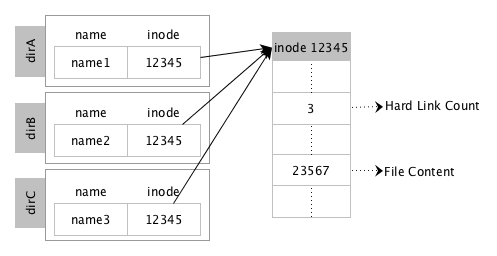
The following diagram illustrates the hard link semantics. Here, directory entries in dirA, dirB, and dirC for file names name1, name2, and name3 respectively all point to the inode 12345, which contains metadata including the text in the file and a count of the number of hard links to the file (or physical data).
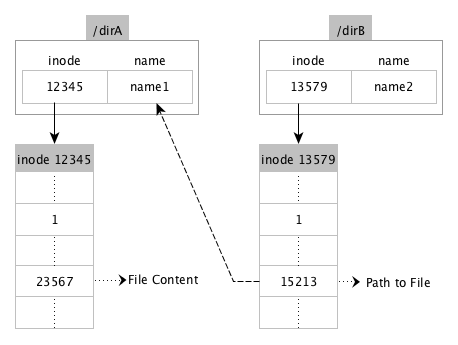
In contrast, when a symbolic link is created, a new inode is created and the text part of the inode (associated with the symlink file) contains the path to the actual file. The following diagram illustrates the symbolic link semantics. Here, the directory entry in dirA for file name, name1, is associated with inode 12345, which contains the text in the file. The directory entry in dirB for symbolic link file, name2, is associated with inode 13579, which contains the path to file in dirA (/dirA/name1). Deleting the file, name1, in dirA will result in the symlink file in dirB, name2, pointing to stale content, which in turn will return errors when accessed.
Hard links can be created on regular files, symlink files, device files, and tables.
Limitations
- Hard links cannot be created on directories.
- Hard links cannot be created across volumes or clusters. Instead, use symbolic link to link to a file on a different volume.
- Hard links within a volume are carried over to mirror volumes and volume snapshots. During cross-mirroring, there will be an error if support for hardlinks is not enabled on both the clusters.
- The
hadoop distcpcommand cannot be used for creating and preserving copies of hard links. - The maximum number of hard links is constrained by the integer width (32 bits), which means the maximum number possible for a file is 232.
Usage
Any user with access to the directory can create a hard link to any file under that directory. To create hard links, the user must have write permissions on the directory and execute permissions (to do the lookup for the path) on the target file. To read or modify the file, the user must have read or write permissions respectively on the file.
Errors
For information on the type of failures and errors, refer to the man page. In addition, please note that the EXDEV error is returned if command is run to create cross-volume or cross-cluster hard links.