Accessing Data with NFS v4
Describes how MapR works with the NFS v4 protocol. Presents an overview of the process flow to read and write MapR processes with NFS v4, and a list of NFS v4 features that MapR does not support.
MapR lets you mount the cluster using NFS v4 so that your applications can read and write data directly. MapR allows direct file modification and multiple concurrent reads and writes using POSIX semantics. With an NFS v4-mounted cluster, you can read and write data directly with standard tools, applications, and scripts. For example, you could run a MapReduce application that outputs to a CSV file, then import the CSV file directly into SQL using NFS v4.
MapR uses NFS Ganesha for supporting NFS v4 features. NFS Ganesha is an Open Source userspace implementation of the NFS v4 server. MapR version 6.1 uses NFS Ganesha version 2.3, while HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric 6.2 uses an upgraded version 3.3 of NFS Ganesha.
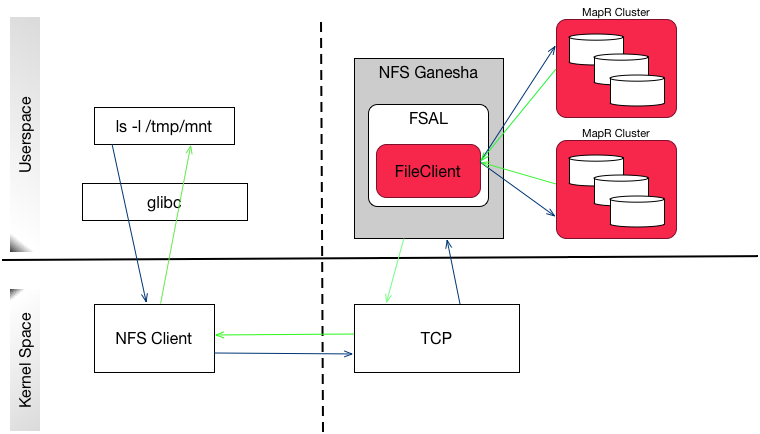
The MapR NFS v4,
running as a userspace process, registers callbacks with NFS Ganesha through the File System
Abstraction Layer (FSAL), which is a shared library (libfsalmapr.so). NFS
Ganesha loads and uses this library whenever the MapR File System is
exported/mounted. The FSAL, in turn, uses FileClient (libMapRClient.so) to
connect to the cluster.
The following diagram illustrates how the MapR processes read and write operations to the MapR cluster using
NFS v4. When the user enters a command (such as ls), the NFS client submits
the request over TCP to the MapR NFS v4 server. The NFS v4 server uses the MapR FileClient to perform the requested operation
on the cluster and returns the response to the NFS v4 client over TCP.
MapR exports each
cluster as the directory /mapr/<cluster name> (for example,
/mapr/my.cluster.com). If you create a mount point with the local path
/mapr, then Hadoop FS paths and NFS v4 paths to the cluster are the same.
This makes it easy to work on the same files using NFS v4 and Hadoop. In a multi-cluster
setting, the clusters share a single namespace, and you can see them all by mounting the
top-level /mapr directory.
For NFS v4, MapR also requires alias or pseudo-path, which when specified masks the mount path from the NFS v4 client. MapR's NFS v4 server provides a pseudo-filesystem where only the exported volumes are visible. This is especially useful in scenarios where one or more volumes in the hierarchy should be hidden and not be visible. For more information, see NFS v4 RFC.
Unsupported NFS v4 Features
MapR does not currently support the following NFS v4 features:
- pNFS
- Delegations
- Mandatory locking
- Lock upgrades and downgrades
- Deny share
- Access Control List (ACL)
- Namespaces
- Persistent reply cache
- Data retention
- Attributes such as time_access, FATTR4_ARCHIVE, FATTR4_FILES_AVAIL, FATTR4_FILES_FREE, FATTR4_FILES_TOTAL, FATTR4_FS_LOCATIONS, FATTR4_MIMETYPE, FATTR4_QUOTA_AVAIL_HARD, FATTR4_QUOTA_AVAIL_SOFT, FATTR4_QUOTA_USED, FATTR4_TIME_BACKUP, and FATTR4_ACL